A neuro exam is integral to diagnosing and monitoring various neurological conditions in healthcare. These assessments comprise different elements, such as the evaluation of pupillary reaction, reflex testing, and muscle strength assessment. Among these crucial components is pupil reactivity, which plays a significant role in providing valuable insights into a patient’s neurological health.
in neurological assessments and explore the advancements in related technology.
What is Pupil Reactivity?
Pupil reactivity refers to how a person’s pupils respond to changes in light conditions. The autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary bodily functions and controls pupil size. When light hits the retina, the autonomic nervous system triggers the pupils to constrict or dilate to optimize vision. Pupil response to light stimuli is a key indicator of neurological health. It helps medical professionals evaluate an individual’s nervous system’s integrity.
The Pupillary Light Reflex (PLR)
This reflex is essential for evaluating pupil reactivity and serves as an indicator of healthy brain function. Light enters the eye and stimulates the retina, sending signals to the brain that control pupil size. A properly functioning PLR ensures that the pupils constrict when exposed to light and dilate in darkness, thus maintaining optimal vision.
Assessing Pupil Reactivity
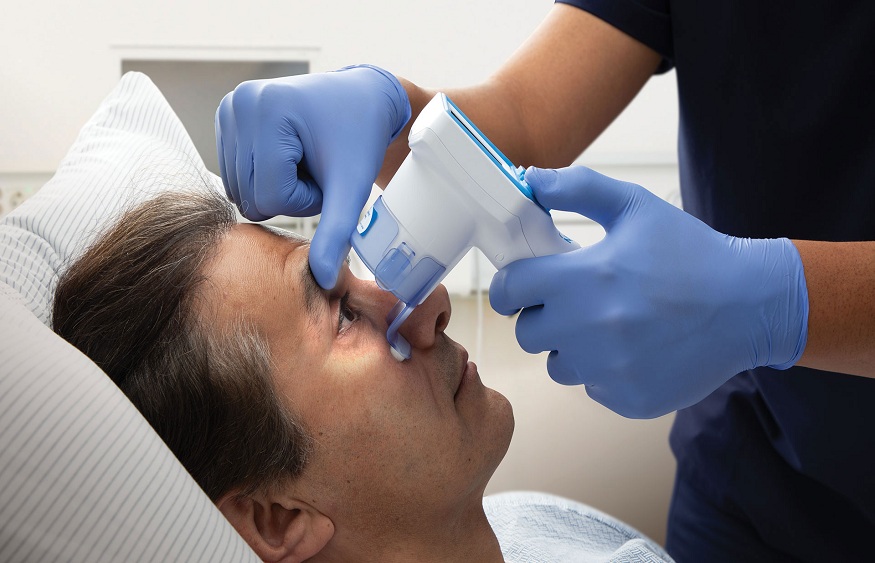
Medical professionals use a penlight or ophthalmoscope to shine light into the patient’s eyes to perform pupil assessment. They observe the consensual response (when the opposite pupil constricts in response to light) and the direct response (when the illuminated pupil constricts) to evaluate the pupils’ reactivity. Additionally, they take note of changes in pupil size and symmetry, which provide further information on a patient’s neurological health.
Normal Pupil Reactivity Findings
Characteristics of normal pupil reactivity include equal and reactive pupils in response to light stimuli. In a well-lit environment, pupils should be constricted, while they should be dilated in darkness. Pupil size may vary between individuals and with different light conditions, but both pupils should be symmetrical and reactive to light for a healthy neurological assessment outcome.
Abnormal Pupil Reactivity Findings
Abnormal pupil reactivity can result from brain injuries, neurological disorders, or other medical conditions. Anisocoria, the presence of unequal pupil sizes, may indicate an underlying issue. Sluggish or nonreactive pupils can also cause concern, as they may suggest potential neurological problems or increased intracranial pressure.
The Relevance of Pupil Reactivity in Neurological Assessments
Evaluating pupil reactivity is relevant in neurological assessments, as it offers vital insights into various aspects of a patient’s neurological health. By assessing the reactivity of pupils to light, healthcare professionals can effectively evaluate the function of cranial nerves II (optic) and III (oculomotor). These nerves play a crucial role in vision and eye movement. Any impairment could indicate potential brain damage or increased intracranial pressure.
Pupil reactivity is also essential in detecting early signs of neurological disorders or injuries, such as stroke, traumatic brain injury, or inflammation. By identifying abnormal pupillary responses, medical professionals can promptly initiate appropriate interventions and treatment plans, potentially preventing further complications and improving patient outcomes.
Limitations of Pupil Reactivity Assessment
Age, medications, or eye conditions can affect pupil size, making accurate assessment challenging. Considering the overall clinical picture and employing complementary diagnostic tools to accurately evaluate a patient’s neurological health is crucial.
Advancements in Pupil Reactivity Assessment Technology
Technological advancements have led to the development of automated NPi pupillometers, improving accuracy and objectivity in measuring pupil reactivity. These devices can be integrated into telemedicine platforms, allowing remote neurological assessments and expanding access to specialized care. Adopting automated pupillometry in clinical practice can enhance the precision of pupil reactivity evaluation, making it a valuable addition to traditional neurological tools.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, pupil reactivity is crucial in neurological assessments, providing essential information about a patient’s nervous system’s integrity. Understanding and recognizing normal and abnormal findings can help medical professionals detect potential issues and monitor treatment effectiveness.