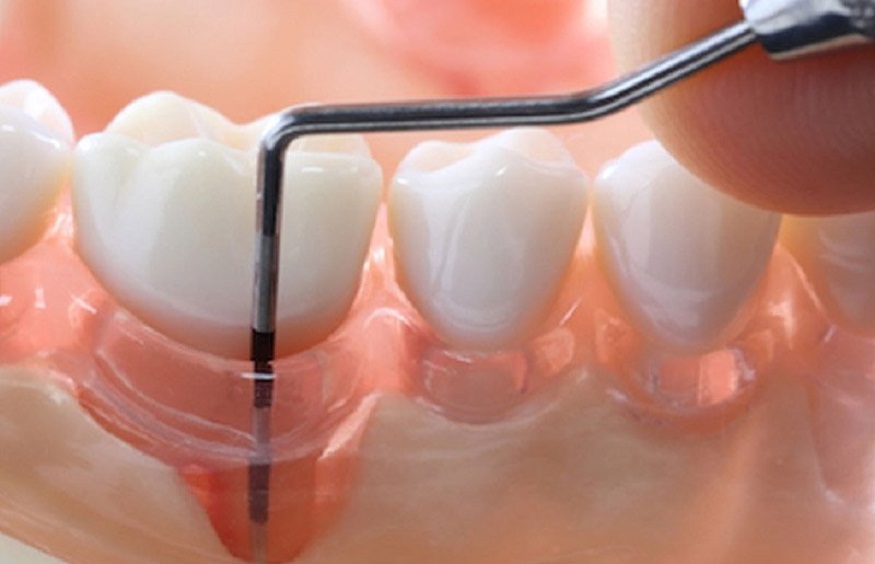
Periodontal disease, a chronic bacterial infection affecting millions, can lead to tooth loss and systemic health issues if left untreated. Dentists emphasize the importance of understanding the stages of periodontal disease to prevent and manage this condition effectively. From mild gingivitis to advanced periodontitis, each stage presents distinct symptoms and requires tailored treatment. By recognizing the signs and seeking professional care from a qualified dentist Hollywood, CA, individuals can halt disease progression, restore oral health, and maintain a radiant smile.
In this article, we will explore the stages of periodontal disease, their characteristics, and management strategies, providing valuable insights for patients seeking comprehensive dental care.
What is Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a chronic bacterial infection that affects the gums, periodontal ligaments, and bone supporting the teeth. Characterized by inflammation and damage to the periodontium, the tissue surrounding the teeth, periodontal disease progresses from mild gingivitis to severe periodontitis if left untreated.
What Causes Periodontal Disease?
Here are the causes of periodontal disease:
Primary Causes
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing.
- Bacterial Accumulation: Plaque and tartar buildup.
- Smoking and Tobacco Use: Increases risk and severity.
Contributing Factors
- Genetics: Family history of periodontal disease.
- Diabetes: Uncontrolled blood sugar levels.
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, menopause, and puberty.
- Medications: Certain medications (e.g., steroids, antidepressants).
- Nutrition: Poor diet, vitamin deficiencies.
- Stress: Weakened immune system.
- Age: Increased risk with age.
Other Factors
- Grinding and Clenching (Bruxism)
- Poor Dental Work (e.g., ill-fitting fillings)
- Gum Recession
- Dental Ignorance or Neglect
What Are The Stages of Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal stages can be classified into the following stages:
Stage 1: Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of periodontal disease, characterized by inflammation of the gums (gingiva).
Symptoms
- Redness and swelling of the gums
- Bleeding when brushing or flossing
- Bad breath (halitosis)
- Loose teeth
Treatment
- Professional dental cleaning (prophylaxis)
- Improved oral hygiene habits (brushing and flossing)
- Antibacterial mouthwash
Stage 2: Early Periodontitis
Early periodontitis is a mild form of periodontal disease, characterized by:
- Pocket formation between teeth and gums (1-2 mm)
- Gum recession
- Bone loss (initial stages)
Symptoms
- Increased bleeding when brushing or flossing
- Slight looseness of teeth
- Changes in bite
Treatment
- Scaling and root planing (deep cleaning)
- Antibacterial therapy (systemic or local)
- Occlusal adjustment (bite correction)
Stage 3: Moderate Periodontitis
Moderate periodontitis is characterized by:
- Pocket formation (3-5 mm)
- Significant bone loss
- Gum recession
Symptoms
- Noticeable looseness of teeth
- Shift in bite
- Pain when chewing
Treatment
- Surgical intervention (flap surgery)
- Bone grafting
- Dental restoration (crowns or bridges)
Stage 4: Advanced Periodontitis
Advanced periodontitis is the most severe stage, characterized by:
- Extensive bone loss
- Gum recession
- Loose or shifting teeth
Symptoms
- Severe pain when chewing
- Difficulty speaking or swallowing
- Aesthetic concerns
Treatment
- Surgical intervention (regenerative procedures)
- Dental implant placement
- Prosthetic restoration
How Can You Prevent Periodontal Disease?
Preventing periodontal disease requires a combination of good oral hygiene habits, regular dental check-ups, and a healthy lifestyle. Here are some ways to prevent periodontal disease:
Oral Hygiene Habits
- Brush teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles.
- Use an antibacterial mouthwash.
- Clean teeth gently with a soft-bristled toothbrush.
Regular Dental Check-Ups
- Schedule dental check-ups every 6 months.
- Get professional cleanings (prophylaxis) regularly.
- Address dental issues promptly.
Healthy Lifestyle
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Avoid sugary and processed foods.
- Quit smoking and tobacco use.
- Manage stress.
Final Takeaway
Periodontal disease is a progressive condition that requires prompt attention and treatment. Understanding the stages of periodontal disease enables individuals to seek timely intervention and prevent further damage. By maintaining good oral hygiene habits, attending regular dental check-ups, and seeking professional treatment, individuals can manage periodontal disease and maintain optimal oral health.